|
Periodic Eigendecomposition
|
|
Periodic Eigendecomposition
|
A class to calculate the periodic eigendecomposition of the product of a sequence of matrices. More...
#include <ped.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| MatrixXd | EigVals (MatrixXd &J, const int MaxN=100, const double tol=1e-16, bool Print=true) |
Eigvals() calculate the eigenvalues of the product of a sequence of matrices in the form of 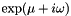 . . | |
| pair< MatrixXd, MatrixXd > | EigVecs (MatrixXd &J, const int MaxN=100, const double tol=1e-16, bool Print=true) |
| calculate the eigenvectors of the product of a sequence of matrices | |
| std::tuple< MatrixXd, vector < int >, MatrixXd > | eigenvalues (MatrixXd &J, const int MaxN=100, const double tol=1e-16, bool Print=true) |
| calculate the periodic Schur decomposition and the eigenvalues of the product of a sequence of matrices. | |
| pair< MatrixXd, vector< int > > | PerSchur (MatrixXd &J, const int MaxN=100, const double tol=1e-16, bool Print=true) |
| Periodic Schur decomposition of a sequence of matrix stored in J. | |
| MatrixXd | HessTrian (MatrixXd &G) |
| vector< int > | PeriodicQR (MatrixXd &J, MatrixXd &Q, const int L, const int U, const int MaxN, const double tol, bool Print) |
| void | Givens (Ref< MatrixXd > A, Ref< MatrixXd > B, Ref< MatrixXd > C, const int k) |
| void | Givens (Ref< MatrixXd > A, Ref< MatrixXd > B, Ref< MatrixXd > C, const Vector2d &v, const int k) |
| Givens rotation with provided 2x1 vector as parameter. | |
| void | HouseHolder (Ref< MatrixXd > A, Ref< MatrixXd > B, Ref< MatrixXd > C, const int k, bool subDiag=false) |
| void | GivensOneIter (MatrixXd &J, MatrixXd &Q, const Vector2d &v, const int L, const int U) |
| void | GivensOneRound (MatrixXd &J, MatrixXd &Q, const Vector2d &v, const int k) |
| vector< int > | checkSubdiagZero (const Ref< const MatrixXd > &J0, const int L, const int U, const double tol) |
| vector< int > | padEnds (const vector< int > &v, const int &left, const int &right) |
| pad two elements at the begining and end of a vector. | |
| double | deltaMat2 (const Matrix2d &A) |
| return the delta of a 2x2 matrix : for [a, b c, d] Delta = (a-d)^2 + 4bc | |
| Vector2d | vecMat2 (const Matrix2d &A) |
| calculate the eigenvector of a 2x2 matrix which corresponds to the larger eigenvalue. Note: MAKE SURE THAT THE INPUT MATRIX HAS REAL EIGENVALUES. | |
| pair< Vector2d, Matrix2d > | complexEigsMat2 (const Matrix2d &A) |
| get the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of 2x2 matrix | |
| int | sgn (const double &num) |
| return the sign of double precision number. | |
| pair< double, int > | product1dDiag (const MatrixXd &J, const int k) |
| pair< Matrix2d, double > | product2dDiag (const MatrixXd &J, const int k) |
| vector< int > | realIndex (const vector< int > &complexIndex, const int N) |
| realIndex() gets the positions of the real eigenvelues from the positions of complex eigenvalues. | |
| vector< Triplet< double > > | triDenseMat (const Ref< const MatrixXd > &A, const size_t M=0, const size_t N=0) |
| triDenseMat() creates the triplets of a dense matrix | |
| vector< Triplet< double > > | triDenseMatKron (const size_t I, const Ref< const MatrixXd > &A, const size_t M=0, const size_t N=0) |
| triDenseMat() creates the triplets of the Kroneck product of an IxI identity matrix and a dense matrix: Identity x R | |
| vector< Triplet< double > > | triDiagMat (const size_t n, const double x, const size_t M=0, const size_t N=0) |
| triDiagMat() creates the triplets of a diagonal matrix. | |
| vector< Triplet< double > > | triDiagMatKron (const size_t I, const Ref< const MatrixXd > &A, const size_t M=0, const size_t N=0) |
| triDiagMat() creates the triplets of the product of a matrix and an IxI indentity matrix. | |
| pair< SparseMatrix< double > , VectorXd > | PerSylvester (const MatrixXd &J, const int &P, const bool &isReal, const bool &Print) |
| perSylvester() create the periodic Sylvester sparse matrix and the dense vector for the reordering algorithm. | |
| MatrixXd | oneEigVec (const MatrixXd &J, const int &P, const bool &isReal, const bool &Print) |
| calculate eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue at postion P given the Periodic Real Schur Form. | |
| void | fixPhase (MatrixXd &EigVecs, const VectorXd &realComplexIndex) |
| fix the phase the complex eigenvectors | |
| void | reverseOrder (MatrixXd &J) |
| Reverse the order of columns of a matrix. | |
| void | reverseOrderSize (MatrixXd &J) |
| Reverse the order of a matrix and also resize it. | |
A class to calculate the periodic eigendecomposition of the product of a sequence of matrices.
| pair< Vector2d, Matrix2d > PED::complexEigsMat2 | ( | const Matrix2d & | A | ) |
get the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of 2x2 matrix
Eigenvalue is stored in exponential way : e^{mu + i*omega}. Here, omega is guarantted to be positive in [0, PI]. The real and imaginary parts are splitted for eigenvector: [real(v), imag(v)] Only one eigenvalue and corresponding eigenvector are return. The other one is the conjugate.
Example: for matrix [1, -1 1, 1], it returns [ 0.346, 0.785] and [-0.707, 0 0 0.707 ] Note : make sure that the input matrix has COMPLEX eigenvalues.
| std::tuple< MatrixXd, vector< int >, MatrixXd > PED::eigenvalues | ( | MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int | MaxN = 100, |
||
| const double | tol = 1e-16, |
||
| bool | Print = true |
||
| ) |
calculate the periodic Schur decomposition and the eigenvalues of the product of a sequence of matrices.
| MatrixXd PED::EigVals | ( | MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int | MaxN = 100, |
||
| const double | tol = 1e-16, |
||
| bool | Print = true |
||
| ) |
Eigvals() calculate the eigenvalues of the product of a sequence of matrices in the form of 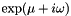 .
.
It returns a [N,3] matrix, with the first column stores 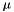 , the second column stores
, the second column stores 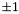 for real eigenvalues or
for real eigenvalues or 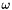 for complex eigenvalues, and the third column states whether the eigenvalue is real (0) or complex (1).
for complex eigenvalues, and the third column states whether the eigenvalue is real (0) or complex (1).
Example usage:
MatrixXd J3 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J2 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J1 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J(5,15); J << J3, J2, J1; PED ped; MatrixXd eigvals = ped.Eigvals(J, 1000, 1e-16, false); cout << eigvals << endl << endl;
The above code return the eigenvalues of 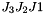 in the format of
in the format of 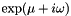 .
.
| [in] | MaxN | Maximal number of periodic QR iteration. |
| [in] | J | a sequence of matrices. Dimension [N, N*M]. |
| [in] | tol | Tolerance used to check the convergence of the iteration process. |
| [in] | Indicate whether to print the intermediate information. |
| pair< MatrixXd, MatrixXd > PED::EigVecs | ( | MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int | MaxN = 100, |
||
| const double | tol = 1e-16, |
||
| bool | Print = true |
||
| ) |
calculate the eigenvectors of the product of a sequence of matrices
Suppose Input matrix 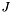 is a sequence of matrices with the same dimension [N,N]:
is a sequence of matrices with the same dimension [N,N]: ![$[J_M, J_{M-1}, \cdots, J_1]$](form_10.png) . Function PED::EigVecs() will return you two matrices.
. Function PED::EigVecs() will return you two matrices.
The first one is the eigen-matrix, for the specific format, see PED::EigVals(). The second matrix has dimension [N*N, M]. The first column stores the eigenvectors of product 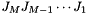 stacked up-down
stacked up-down ![$[v_1, v_2,\cdots,v_M]^{\top}$](form_20.png) . The second column stores the eigenvectors of product
. The second column stores the eigenvectors of product 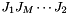 , and similarly, for the remaining columns.
, and similarly, for the remaining columns.
 and
and  vectors are complex pair, then elements from
vectors are complex pair, then elements from 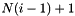 to
to 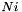 is the real part, and elements from
is the real part, and elements from 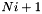 to
to 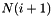 is the imaginary part. They are stored in this way for better usage of memory.
is the imaginary part. They are stored in this way for better usage of memory.Example usage:
MatrixXd J3 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J2 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J1 = MatrixXd::Random(5,5); MatrixXd J(5,15); J << J3, J2, J1; PED ped; std::pair<MatrixXd, MatrixXd> eigs = ped.Eigvals(J, 1000, 1e-16, false); cout << eigs.first << endl << endl; // print eigenvalues cout << eigs.second << endl << endl; // print eigenvectors.
The above code return the eigenvalues (in the format of 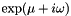 ) and eigenvectors of
) and eigenvectors of 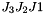 ,
, 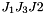 ,
, 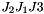 .
.
| [in] | MaxN | Maximal number of periodic QR iteration. |
| [in] | J | a sequence of matrices. Dimension [N, N*M]. |
| [in] | tol | Tolerance used to check the convergence of the iteration process. |
| [in] | Indicate whether to print the intermediate information. |
| void PED::fixPhase | ( | MatrixXd & | EigVecs, |
| const VectorXd & | realComplexIndex | ||
| ) |
fix the phase the complex eigenvectors
The complex eigenvectors got from periodic eigendecompostion are not fixed becuase of the phase invariance. This method will make the first element of each complex eigenvector be real.
| [in,out] | EigVecs | Sequence of eigenvectors got from periodic eigendecomposition |
| [in] | realCompelxIndex | A vector indicating whether a vector is real or complex (third column of eigenvalues got fromx periodic eigendecomposition). |
| void PED::Givens | ( | Ref< MatrixXd > | A, |
| Ref< MatrixXd > | B, | ||
| Ref< MatrixXd > | C, | ||
| const Vector2d & | v, | ||
| const int | k | ||
| ) |
Givens rotation with provided 2x1 vector as parameter.
| MatrixXd PED::oneEigVec | ( | const MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int & | P, | ||
| const bool & | isReal, | ||
| const bool & | |||
| ) |
calculate eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue at postion P given the Periodic Real Schur Form.
The eigenvectors are not normalized, and they correspond to matrix products: JmJm-1..J1, J1JmJm-1..J2, J2J1Jm...J3, ...
| vector< int > PED::padEnds | ( | const vector< int > & | v, |
| const int & | left, | ||
| const int & | right | ||
| ) |
pad two elements at the begining and end of a vector.
| vector< int > PED::PeriodicQR | ( | MatrixXd & | J, |
| MatrixXd & | Q, | ||
| const int | L, | ||
| const int | U, | ||
| const int | MaxN, | ||
| const double | tol, | ||
| bool | |||
| ) |
PeriodicQR transforms an unreduced hessenberg-triangular sequence of matrices into periodic Schur form. This iteration method is based on the Implicit-Q theorem.
| pair< MatrixXd, vector< int > > PED::PerSchur | ( | MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int | MaxN = 100, |
||
| const double | tol = 1e-16, |
||
| bool | Print = true |
||
| ) |
Periodic Schur decomposition of a sequence of matrix stored in J.
| pair< SpMat, VectorXd > PED::PerSylvester | ( | const MatrixXd & | J, |
| const int & | P, | ||
| const bool & | isReal, | ||
| const bool & | |||
| ) |
perSylvester() create the periodic Sylvester sparse matrix and the dense vector for the reordering algorithm.
| J | the sequence of matrix in order: Jm, Jm-1,... J1 |
| P | the position of the eigenvalue |
| isReal | for real eigenvector; otherwise, complex eigenvector |
| vector< int > PED::realIndex | ( | const vector< int > & | complexIndex, |
| const int | N | ||
| ) |
realIndex() gets the positions of the real eigenvelues from the positions of complex eigenvalues.
Denote the sequence of complex positions: [a_0, a_1,...a_s], then the real positions between [a_i, a_{i+1}] is from a_i + 2 to a_{i+1} - 1. Example: Complex positions : 3, 7, 9 Dimension : N = 12 ==> Real positions : 0, 1, 2, 5, 6, 11
| void PED::reverseOrder | ( | MatrixXd & | J | ) |
Reverse the order of columns of a matrix.
J = [j1,j2,...jm] => [Jm, jm-1, ..., j1]
| [in,out] | the | matrix that need to be reversed in place. |
| void PED::reverseOrderSize | ( | MatrixXd & | J | ) |
Reverse the order of a matrix and also resize it.
We usually squeeze the input such that each column represents one of the members of a sequence of matrices. reverseOrderSize() will first reverse the order and then resize it to the right format. Eg: [j1,j2,...jm] => [jm jm-1,...j1] with dimension [N^2, M] => dimension[N,N*M]
| [in,out] | J | The matrix that need to be reversed and re-sized in place. |
| vector< Tri > PED::triDenseMat | ( | const Ref< const MatrixXd > & | A, |
| const size_t | M = 0, |
||
| const size_t | N = 0 |
||
| ) |
triDenseMat() creates the triplets of a dense matrix
| vector< Tri > PED::triDenseMatKron | ( | const size_t | I, |
| const Ref< const MatrixXd > & | A, | ||
| const size_t | M = 0, |
||
| const size_t | N = 0 |
||
| ) |
triDenseMat() creates the triplets of the Kroneck product of an IxI identity matrix and a dense matrix: Identity x R
| vector< Tri > PED::triDiagMat | ( | const size_t | n, |
| const double | x, | ||
| const size_t | M = 0, |
||
| const size_t | N = 0 |
||
| ) |
triDiagMat() creates the triplets of a diagonal matrix.
| vector< Tri > PED::triDiagMatKron | ( | const size_t | I, |
| const Ref< const MatrixXd > & | A, | ||
| const size_t | M = 0, |
||
| const size_t | N = 0 |
||
| ) |
triDiagMat() creates the triplets of the product of a matrix and an IxI indentity matrix.
 1.7.6.1
1.7.6.1